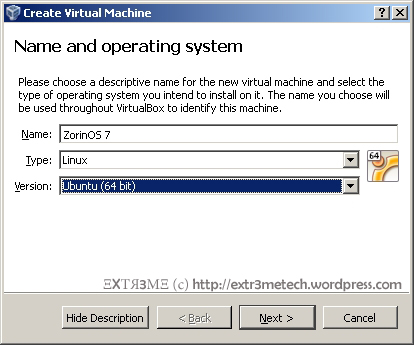
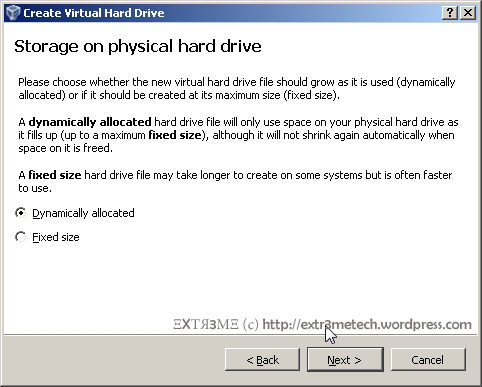
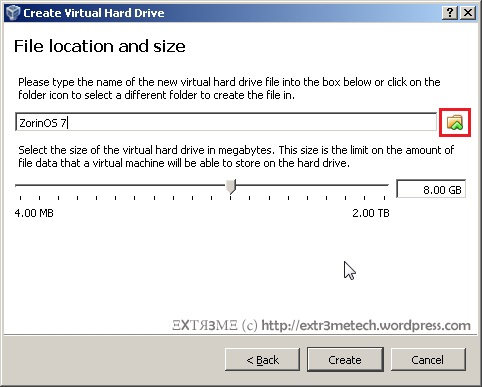
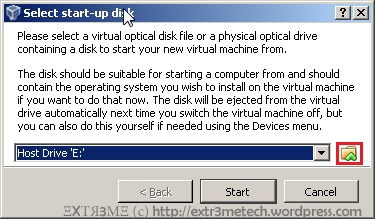
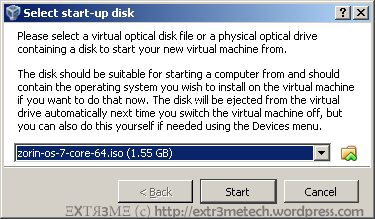
Hi guys, this is a post on creating a simple text mode menu in Python 2.7.x. Hope this helps! Below is the output of the sample menu that we will be creating:
Sample Menu
------------------------------ MENU ------------------------------ 1. Menu Option 1 2. Menu Option 2 3. Menu Option 3 4. Menu Option 4 5. Exit ------------------------------------------------------------------- Enter your choice [1-5]:
Here we have a function print_menu() which is used only to print the menu and the options available. This function does not take any inputs.
The source we have here creates a menu with 5 options with the 5th option to exit the menu.
Here, we create a Boolean variable named “loop” and set its value to “True“. Then we create a while loop which will run until the value of “loop” is “False”.
And within the while loop, we call the function print_menu() in which the user is presented with a menu and the list of options. We now request the user input and store it in a variable named “choice” [NOTE: The input must be a number and not any character or else it will through a error].
Now, we use create if statements to check the value of choice. For example: the first if statement checks if choice==1 and if it prints “Menu 1 has been selected”. Similar, We make use of elif statements to check other values of choice.
And when choice==5, we change the value of “loop” to “False” , which will end the while loop as it will only run when the value of “loop” is “True“.
Finally, for all other numbers other than 1,2,3,4 and 5, we simply print and error message and requests the user to enter a valid input and to try again.
Source Code:
## Text menu in Python
def print_menu(): ## Your menu design here
print 30 * "-" , "MENU" , 30 * "-"
print "1. Menu Option 1"
print "2. Menu Option 2"
print "3. Menu Option 3"
print "4. Menu Option 4"
print "5. Exit"
print 67 * "-"
loop=True
while loop: ## While loop which will keep going until loop = False
print_menu() ## Displays menu
choice = input("Enter your choice [1-5]: ")
if choice==1:
print "Menu 1 has been selected"
## You can add your code or functions here
elif choice==2:
print "Menu 2 has been selected"
## You can add your code or functions here
elif choice==3:
print "Menu 3 has been selected"
## You can add your code or functions here
elif choice==4:
print "Menu 4 has been selected"
## You can add your code or functions here
elif choice==5:
print "Menu 5 has been selected"
## You can add your code or functions here
loop=False # This will make the while loop to end as not value of loop is set to False
else:
# Any integer inputs other than values 1-5 we print an error message
raw_input("Wrong option selection. Enter any key to try again..")
Feel feel to leave a comment if you have any queries or want to reach out to me. You can also Follow/Subscribe to my blog to get future blog posts! Happy Bloggin! 🙂
Regards
ΞXΤЯΞМΞ